Operating Model Template in Financial Analysis
The operating model is a vital framework in financial analysis that defines how a business generates value through its operations. It integrates various components, such as revenue streams, cost structures, and resource allocation, to provide a comprehensive view of the organization's financial health. By employing an operating model, analysts can assess performance, identify inefficiencies, and make informed decisions to optimize resource utilization. This model not only supports strategic planning but also enhances forecasting accuracy and financial reporting, ultimately driving sustainable growth.Operating Model Template for Excel: Key Components
The Operating Models typically used by businesses are built on the following key components:- Strategy: The operating model must align with the company's overall strategy, detailing how operational activities will help achieve strategic goals.
- Structure: This defines the organization’s hierarchy, including reporting relationships and departmental roles, clarifying accountability.
- Processes: It outlines the key workflows that drive business functions, from product development to customer service.
- Technology: The model specifies the necessary technological infrastructure to support operations.
- People: It identifies the skills and roles required for the workforce.
- Culture: This aspect shapes employee interactions and the organization's identity, influencing how business is conducted.
Types of Operating Models for Excel in Financial Analysis
Companies use various types of operating models for financial analysis, including:- Top-Down Model: This approach starts with high-level revenue projections and breaks them down into operational components.
- Bottom-Up Model: This model builds forecasts from detailed operational inputs, such as unit sales and cost structures.
- Activity-Based Model: Focuses on specific activities that drive costs and revenues, helping identify efficiencies.
- Zero-Based Budgeting: Requires justifying all expenses for each new period, rather than adjusting previous budgets.
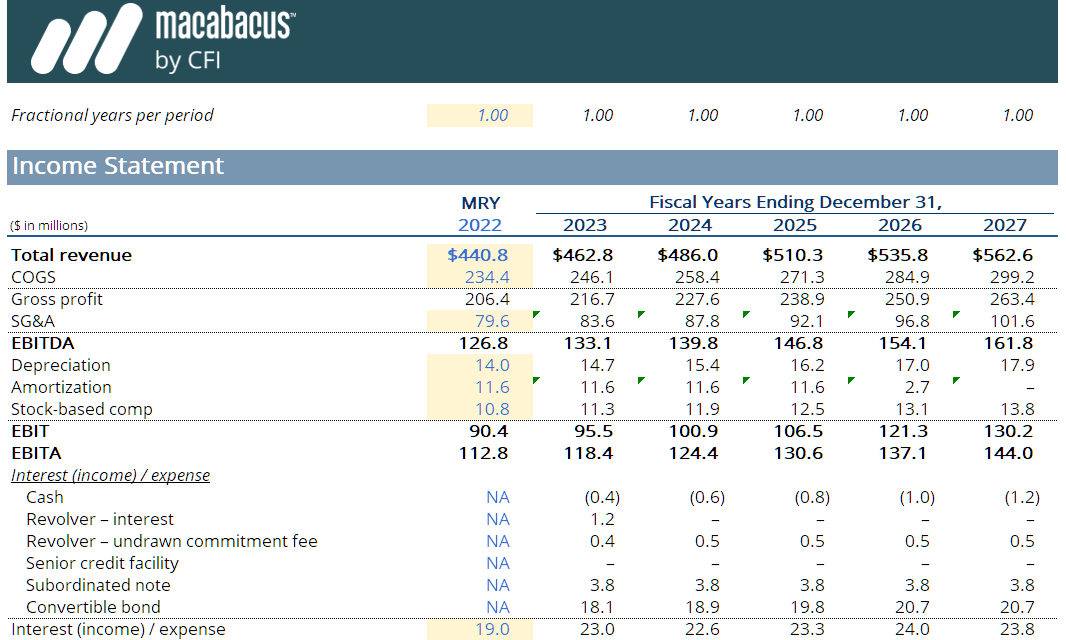
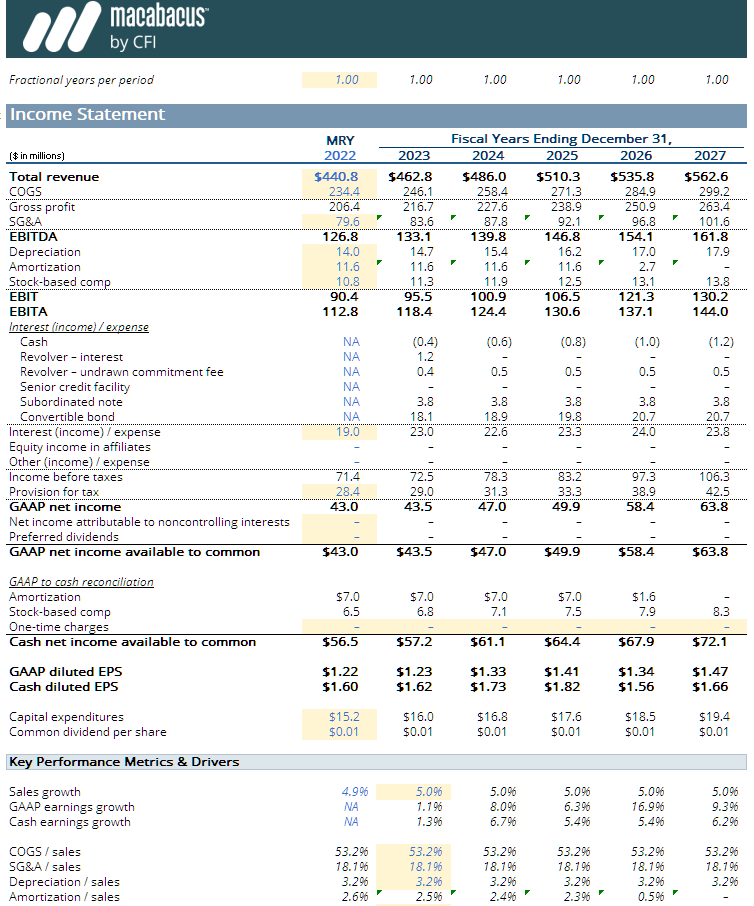
Operating Model Template: The Power of the Macabacus Financial Model
The Macabacus operating model implements key accounting and tax concepts and is a foundational building block for our merger and LBO models. Advanced concepts include deferred taxes, equity method accounting for investments, Dividends Received Deduction (DRD), net operating losses (NOL), pay-in-kind (PIK) interest, alternative minimum tax (AMT), and more.The Macabacus financial model stands as a cornerstone of advanced financial analysis, blending precision and versatility to meet the demands of modern Macabacus modeling. By simplifying intricate calculations and maintaining accuracy, the Macabacus financial model empowers professionals to make informed decisions and achieve strategic financial objectives with confidence.